SteerVLM: Robust Model Control through Lightweight Activation Steering for Vision-Language Models
Anushka Sivakumar, Andrew Zhang, Zaber Hakim, Chris Thomas
[Virginia Tech  ]
]
🌟 Published in Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025 🌟
Abstract
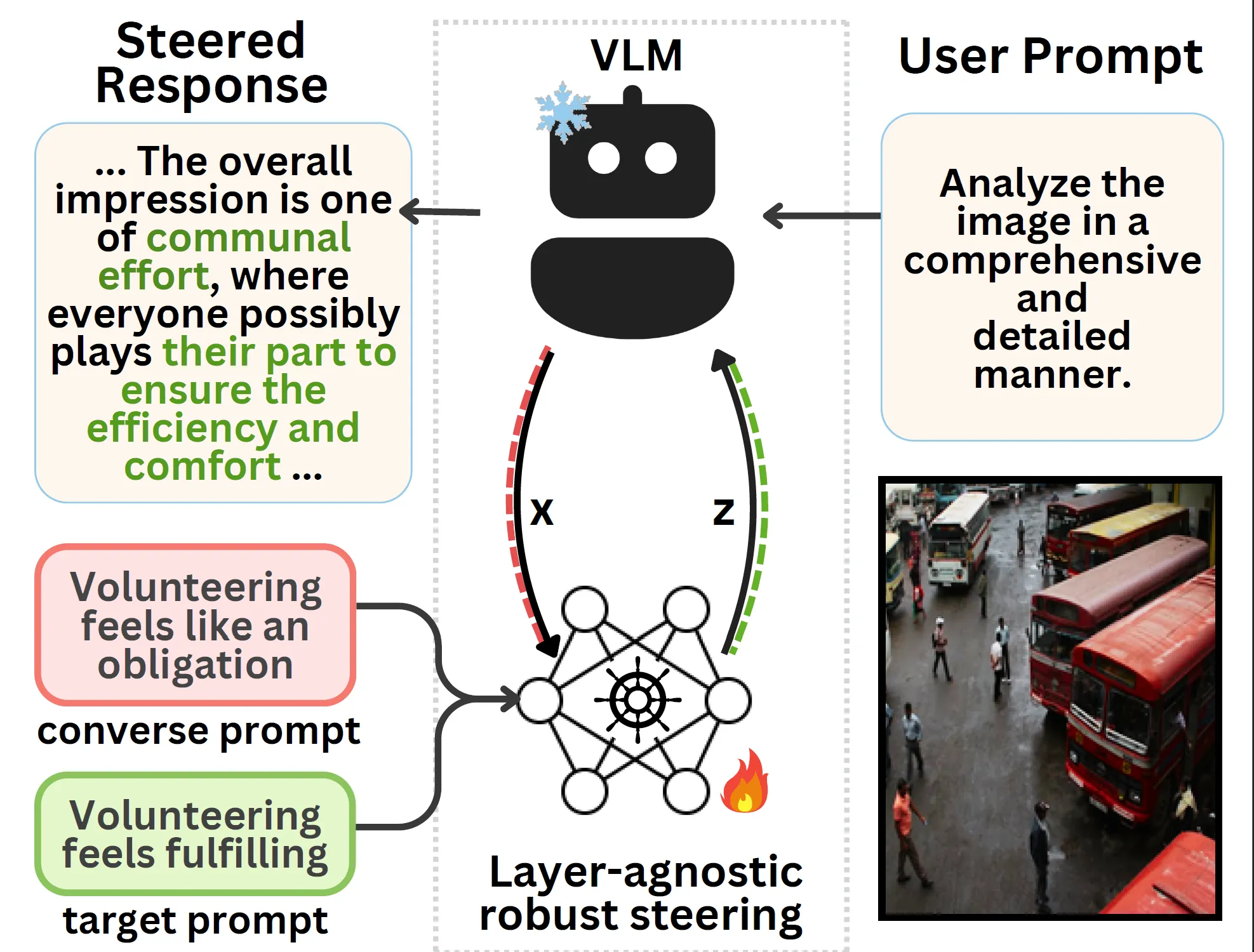
This work introduces SteerVLM, a lightweight steering module designed to guide Vision Language Models (VLMs) towards outputs that better adhere to desired instructions. Our approach learns from the latent embeddings of paired prompts encoding target and converse behaviors to dynamically adjust activations connecting the language modality with image context. This provides fine-grained, inference-time control over complex output semantics without modifying model weights while preserving performance on off-target tasks. Our steering module gains model control via dimension-wise activation modulation and adaptive layer-wise steering without requiring pre-extracted static vectors or manual tuning of intervention points. Furthermore, we introduce VNIA (Visual Narrative Intent Alignment), a multimodal dataset specifically created to facilitate the development and evaluation of VLM steering techniques. Our method outperforms existing intervention techniques on steering and hallucination mitigation benchmarks for VLMs and proposes a robust solution for multimodal model control through activation engineering.
Methodology
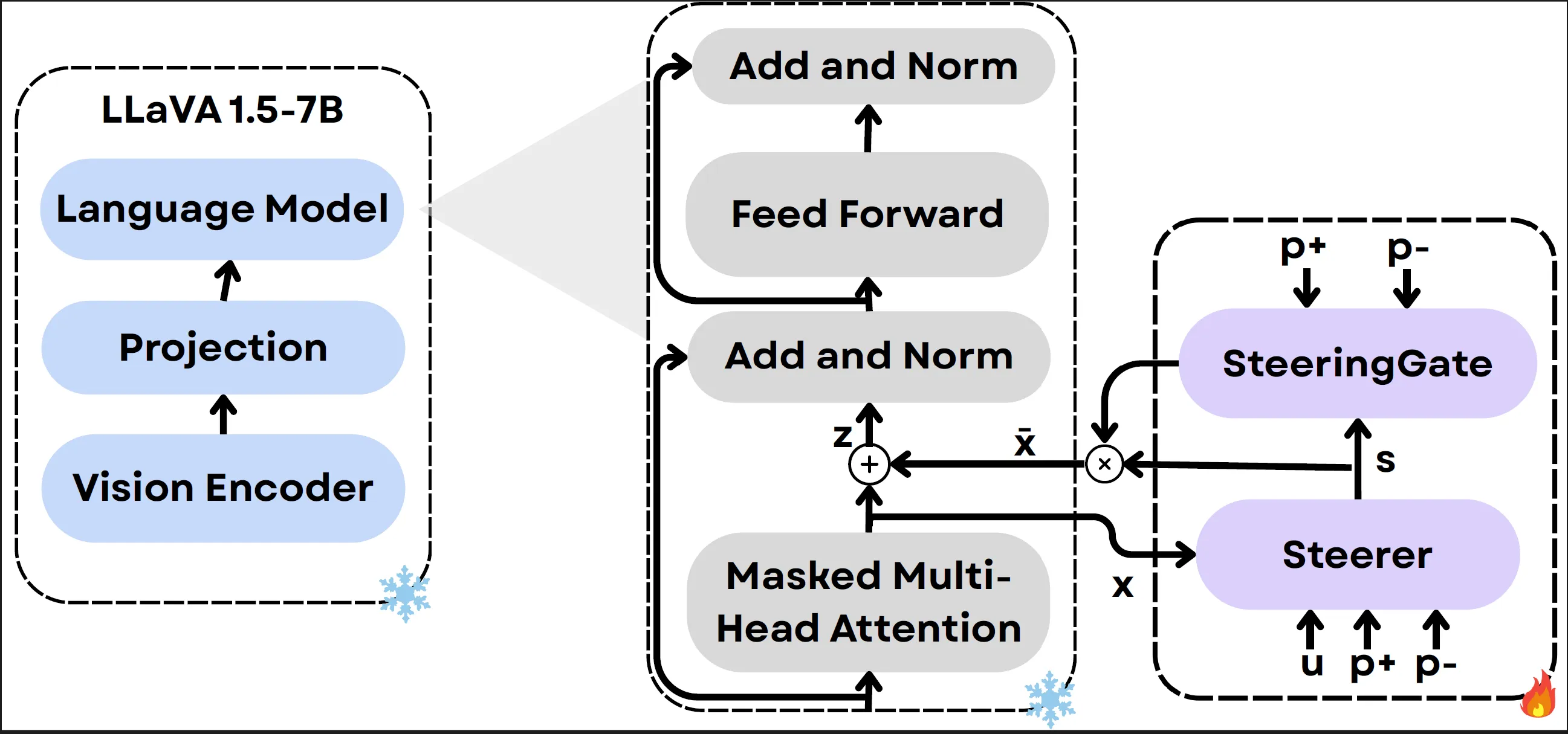
The SteerVLM module is hooked into the VLM’s language decoder right after the multi-head attention layer, where it modulates the post-attention activations enabling fine-grained, layer-agnostic steering.
The Steerer (Attention module) calculates the required activation shift, the SteeringGate (MLP with gate) regulates its intensity per dimension.
The Steering Module:
- Learns non-linear mapping between target and converse prompts.
- Layer-agnostic and dimension-wise adaptive steering.
- Operates at inference time, with no static / pre-determined steering vectors.
Results
Quantitative Results
| Model | sv1 | sv2 | sv3 | sv4 | sv5 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML-ACT (Rodriguez et al., 2024) | 0.46 | 0.475 | 0.485 | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.47 |
| MLLM Steering (Khayatan et al., 2025) | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.51 | 0.485 | 0.535 | 0.51 |
| CAA (Rimsky et al., 2024) | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.61 | 0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 |
| Contrastive / layer * | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.54 |
| Act Add (Turner et al., 2023) | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.59 | 0.475 | 0.58 | 0.55 |
| ACT (Wang et al., 2025) | 0.56 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.535 | 0.59 | 0.55 |
| Ours | 0.84 | 0.69 | 0.83 | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.71 |
Table 1: SteerVLM outperforms existing steering methods in a Zero-shot setting (unseen; no pre-trained or pre-computed steering vectors or prompts for inference) - with GPT o4-mini as VLM as a judge.
| Model | Zero-shot | Accuracy / F1-Score (Adversarial) | Popular | Random | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLaVA1.5-7B Zero-shot (Liu et al., 2024a) | ✓ | 79.8 / 81.7 | 85.5 / 86.1 | 88.3 / 88.8 | 84.5 / 85.5 |
| ML-ACT (Rodriguez et al., 2024) | ✗ | 79.8 / 75.7 | 80.8 / 76.6 | 81.1 / 76.8 | 80.6 / 76.4 |
| MLLM Steering (Khayatan et al., 2025) | ✗ | 72.4 / 76.1 | 76.9 / 79.1 | 78.4 / 80.5 | 75.9 / 78.6 |
| CAA (Rimsky et al., 2024) | ✗ | 53.0 / 68.0 | 54.9 / 68.9 | 60.6 / 71.6 | 56.2 / 69.5 |
| Contrastive / layer | ✓ | 79.8 / 81.8 | 85.7 / 86.4 | 89.3 / 89.4 | 84.9 / 85.7 |
| Act Add (Turner et al., 2023) | ✓ | 79.2 / 81.3 | 85.7 / 86.3 | 89.3 / 89.5 | 84.7 / 85.7 |
| ACT (Wang et al., 2025) | ✗ | 79.0 / 80.7 | 85.5 / 85.9 | 89.0 / 88.9 | 84.5 / 85.1 |
| Ours | ✓ | 81.5 / 82.5 | 87.6 / 87.7 | 90.2 / 90.1 | 86.4 / 86.8 |
Table 2: SteerVLM is task transferable, tuned on topic dataset, but outperforms existing methods Zero-shot (unseen; no pre-trained or pre-computed steering vectors or prompts for inference) on hallucination mitigation on the OHD benchmark with POPE metrics.
*More experiments and results can be found in the paper!
Qualitative Analysis and Results
SteerVLM vs. Prompting: SteerVLM integrates desired behavior into the response
Effect of (inference-time) steering strength
VNIA DATASET
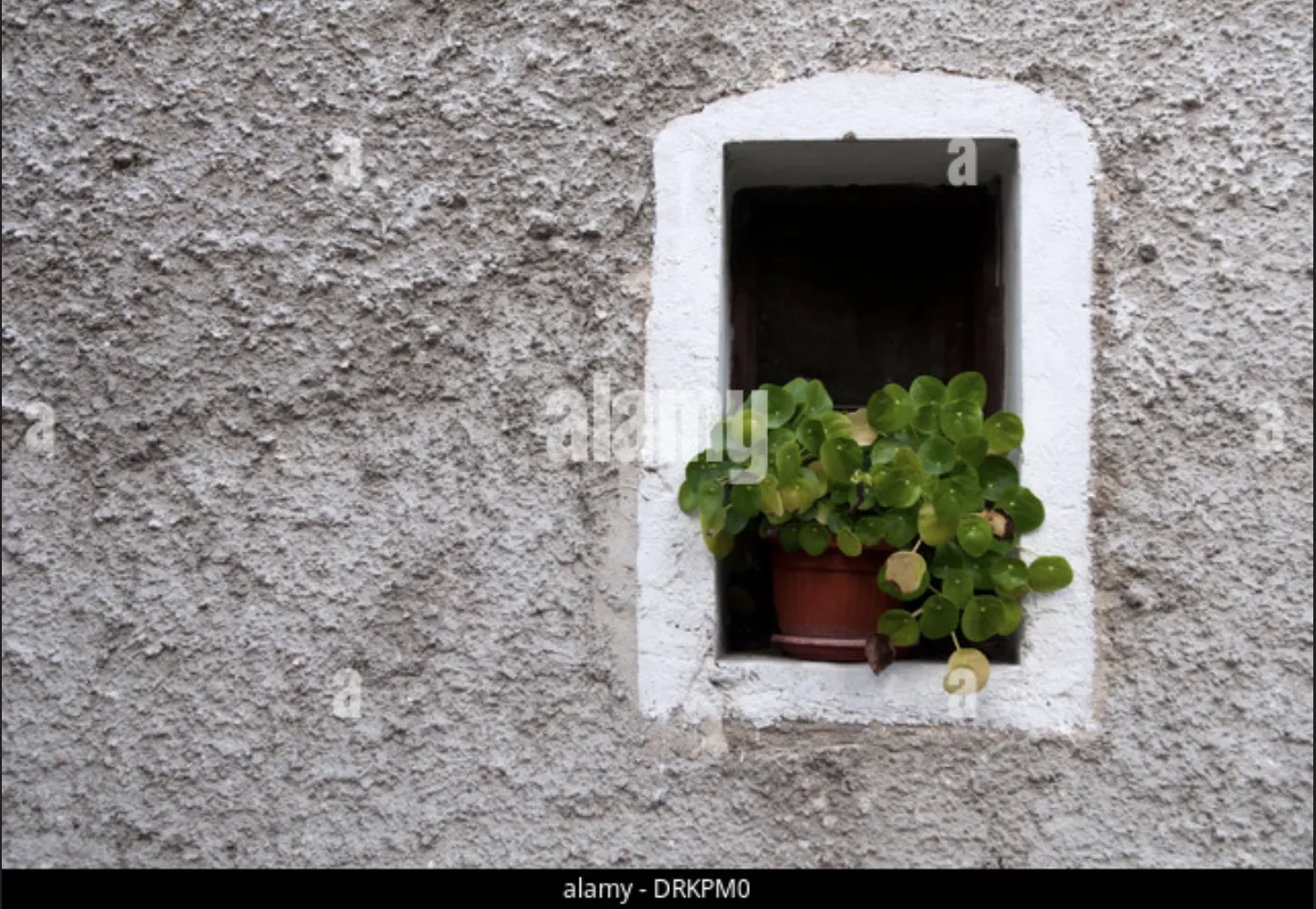
Task: Image description
Target Prompt: "minimalist spaces feel devoid of warmth”
Converse Prompt: "living in minimalist spaces promotes clarity”
Response: "The image portrays a section of a wall with a small, arched opening, containing a terra cotta pot of greenery. One might observe the surrounding wall's textured, neutral tones and the stark simplicity of the scene, appearing to emphasize the lone splash of life amidst an expanse of emptiness. The green leaves seem to cling to the pot, suggesting a yearning for companionship or warmth in the limited space available. The minimal features of the setting could evoke a sense that the area, devoid of additional decorative elements, might feel quiet and possibly isolated. This portrayal may lead some to reflect on how such simplicity in design can influence perceptions of liveliness and coziness in a space.”
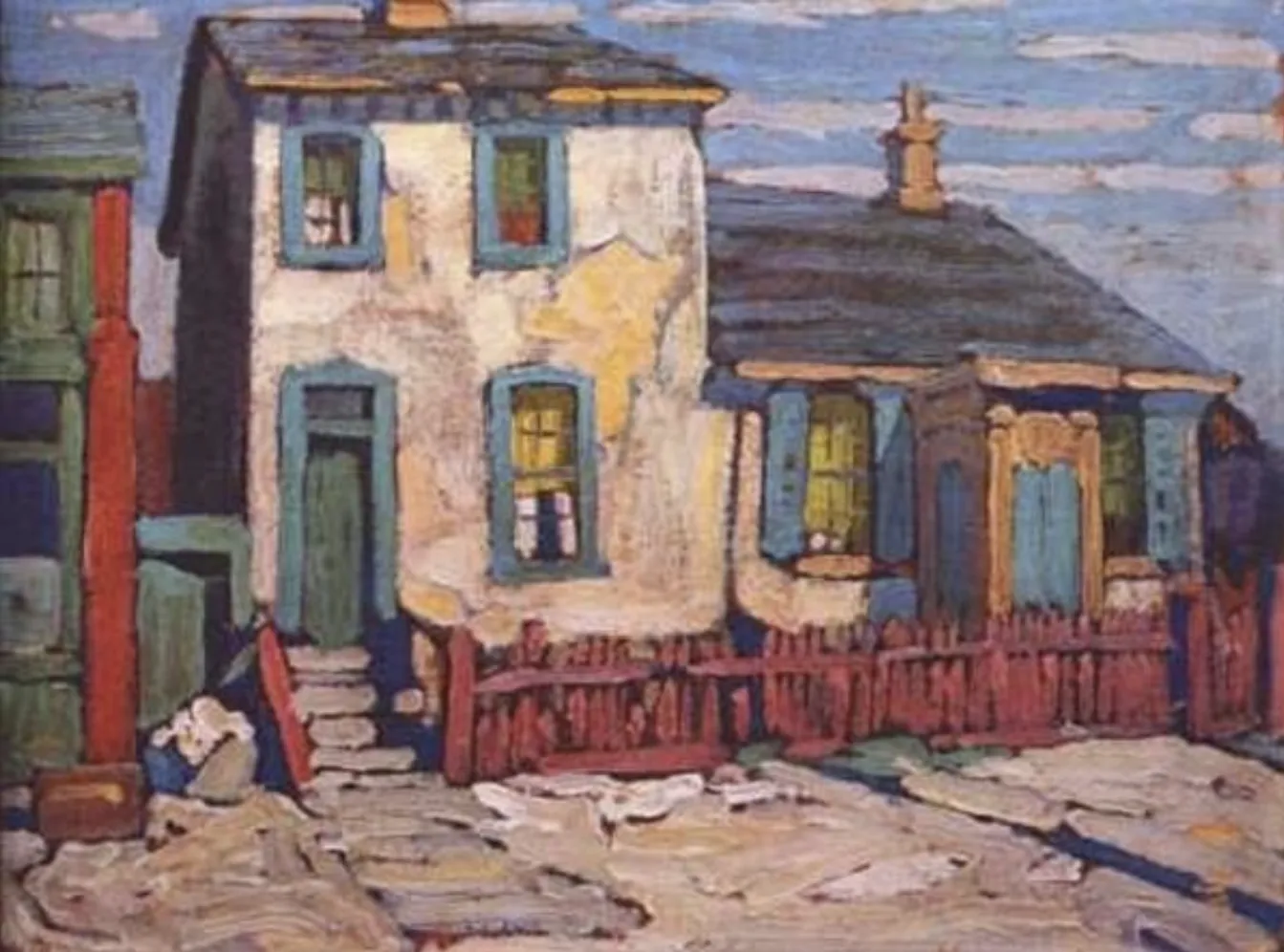
Task: Image description
Target Prompt: "The sound of rain on a tin roof is soft and pleasant”
Converse Prompt: "Rain on a tin roof is too loud and unpleasant”
Response: "The image depicts a quaint, weathered house with a barren yard, appearing to be captured during a period of neglect or transition. Perhaps the dilapidated state suggests an eloquent tale of past liveliness. A short, reddish-brown fence runs alongside the property, possibly serving as a boundary between public and private spaces. The house is painted in muted, pastel hues, with hints of blue and green adorning its windows and doors, creating an impression of faded charm. The artist has used broad strokes that suggest a light touch, much like the soft and gentle essence one might associate with patterns of calm rainfall. The soft interplay of light and shadow on the rooftop could evoke a serene atmosphere, as if nature itself is whispering secrets to the silent dwelling. Outdoors, scattered items and materials indicate an evolving or shifting narrative of the home's purpose, enhancing the subtle narrative of change and resilience in an urban or suburban setting.”
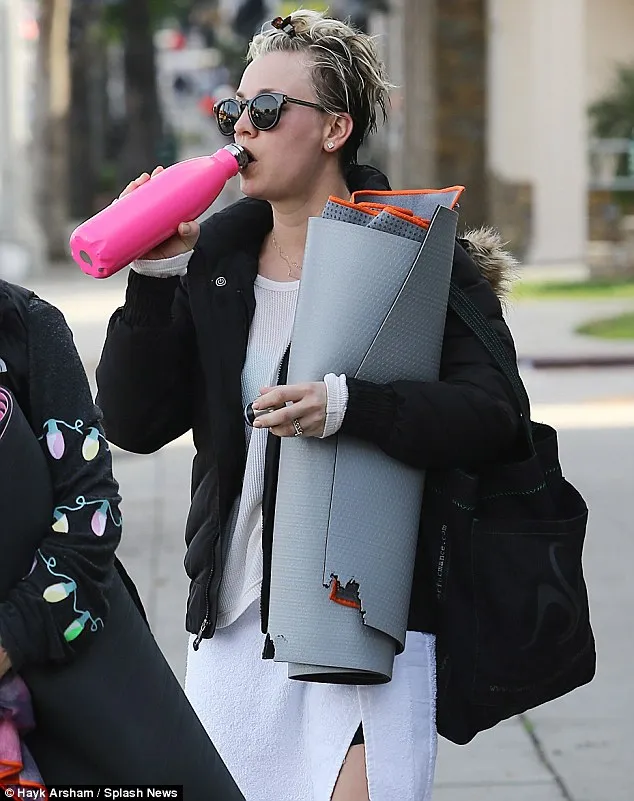
Task: Short story
Target Prompt: "I hate exercising”
Converse Prompt: "I love exercising”
Response: "Clutching a rolled-up mat and a water bottle, she trudged through the street, her gaze focused on the ground. Each step weighed heavier than the last. The pink bottle barely tasted sweet anymore; it was just a necessary stopgap on the way. Her sunglasses reflected the biting cold that matched her mood. The bag on her shoulder felt like a lead anchor, a constant reminder of the inevitable routine ahead. Maybe tomorrow would be different, but for now, she was just maneuvering through the motions."
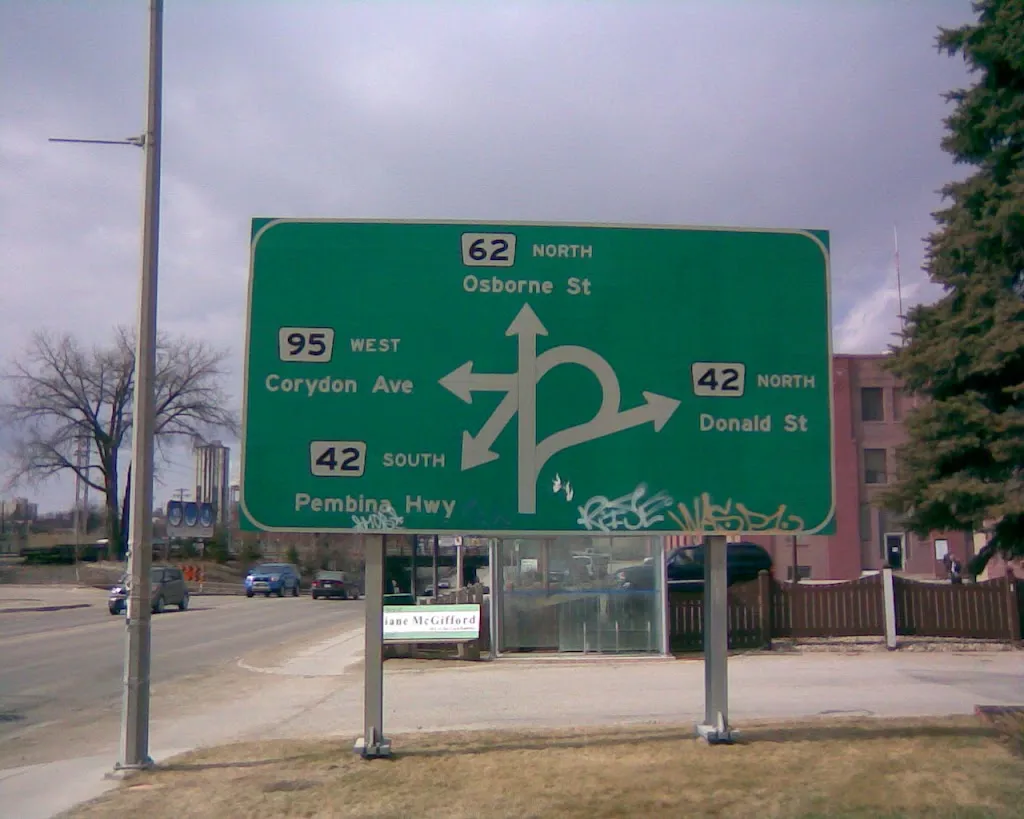
Task: Short story
Target Prompt: "Exploring new cities is exciting”
Converse Prompt: "Exploring new cities is tiring”
Response: "Anna peered at the sprawling green sign, her heart aflutter with possibilities. Each arrow beckoned like a secret, promising tales of winding avenues and bustling streets beyond. Turning left toward Osborne, her mind buzzed with the thrill of unseen journeys, each destination a blank canvas, eager to be painted with new adventures. The way ahead sparkled with the promise of stories yet to be discovered, and the excitement was unmistakable in her eager stride.”
Images taken from Conceptual Caption 3 Million Dataset*
Bibtex
@inproceedings{sivakumar2025steervlm,
title="{S}teer{VLM}: Robust Model Control through Lightweight Activation Steering for Vision Language Models",
author="Sivakumar, Anushka and Zhang, Andrew and Hakim, Zaber and Thomas, Chris",
booktitle="Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2025",
publisher="Association for Computational Linguistics",
year="2025",
url="https://aclanthology.org/2025.findings-emnlp.1285/"
}